
Followup lateral view of neck soft tissue xray that was carried out... Download Scientific
For FBs that have passed beyond this location, radiologic study is recommended, including anteroposterior and lateral neck radiographs (LNRs) using the soft-tissue technique. This is a quick and simple imaging method that in emergency departments achieves detection rates of 70%-80% in assessing FBs in the hypopharynx and upper cervical esophagus.

Lateral radiograph of neck soft tissue shows subcutaneous emphysema... Download Scientific Diagram
The lateral neck x-ray is the main imaging study. The size of the adenoids is less of a consideration than the degree to which they encroach on the nasopharyngeal airway: if no adenoidal tissue after age 6 months, suspect an immune deficiency if enlarged adenoids persist well after childhood, suspect lymphatic malignancy Treatment and prognosis

Soft tissue Xray of the neck, in lateral view, showing large anterior... Download Scientific
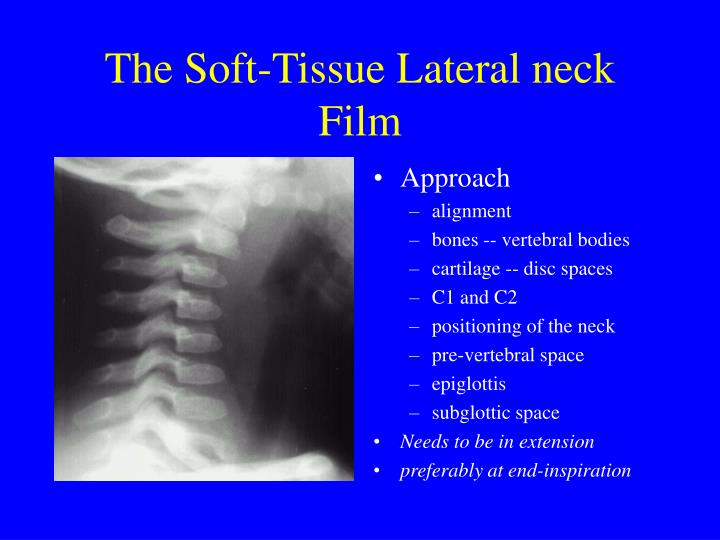
SOFT TISSUE NECK . ROUTINES: AP . and. Lateral of the neck--upright or supine. (We can only charge . for a 1 view). DISTANCE: 40" BUCKY: Yes . FOCAL SPOT: Small . IMAGING PLATE: 10x12 CR cassette or DR detector . CENTRAL RAY: Perpendicular to the film entering the neck at the . level of the thyroid cartilage. Include the entire nasal passage.

Soft Tissue Neck LAT labelled Radiology student, Radiology, Medical anatomy
Age: 6 years Gender: Male x-ray Normal appearances of the soft tissues of the neck. Case Discussion A soft tissue plain radiograph of the neck is usually performed to assess for an ingested foreign body, such as a bone whilst eating. 3 public playlists include this case Related Radiopaedia articles Normal head and neck imaging examples
PEM Blog Briefs Exam based approach to the patient with a sore throat
A neck X-ray, also known as a cervical spine X-ray, is an X-ray image taken of your cervical vertebrae. This includes the seven bones of your neck that surround and protect the top.

A postoperative laterolateral neck Xray in a patient who underwent... Download Scientific
A neck X-ray is a safe and painless test that uses a small amount of radiation to make images of the soft tissues in the neck. During the examination, an X-ray machine sends a beam of radiation through the neck, and an image is recorded on a computer or special film. This image includes structures such as the vertebrae (neck bones), the soft.

Radiograph showing the soft tissues of the neck lateral view The BMJ
Normal soft tissue neck x-ray: lateral projection Case contributed by Henry Knipe Diagnosis certain Share Add to Citation, DOI, disclosures and case data Presentation ?foreign body. Patient Data Age: 35 years Gender: Female x-ray Normal examination. Prevertebral soft tissues are within normal limits. No radiopaque foreign body. Case Discussion

Softtissue neck Xray. (A) Front view and (B) lateral view. Both... Download Scientific Diagram
The neck is a critical anatomical region with a complex structure that supports various functions, including head movement, breathing, and speech. It is susceptible to a range of risks and can be affected by various factors, leading to pain, injury, or functional limitations.
PPT Peds Soft Tissue Neck Xrays PowerPoint Presentation ID518700
What are X-rays of the spine, neck or back? X-rays use invisible electromagnetic energy beams to make images of internal tissues, bones, and organs on film. Standard X-rays are performed for many reasons. These include diagnosing tumors or bone injuries.

Lateral Neck XRay Soft Tissue Anatomy Dr. Devpriyo GrepMed
A neck X-ray can help doctors diagnose problems in the soft tissues. For example, symptoms such as stridor (noisy breathing), barking cough, and hoarseness may be due to swelling of different areas in or near the airway.

Normal lateral soft tissue neck Xray. Download Scientific Diagram
The soft neck tissue x-ray series consists of two images: the anterior-posterior (AP) and the lateral (B). The soft-tissue neck series images are intentionally underexposed to provide better visualization of the soft tissues. A close-up of these images is shown in Figure 4-2. Abnormalities of the retropharyngeal space can be indicative of.

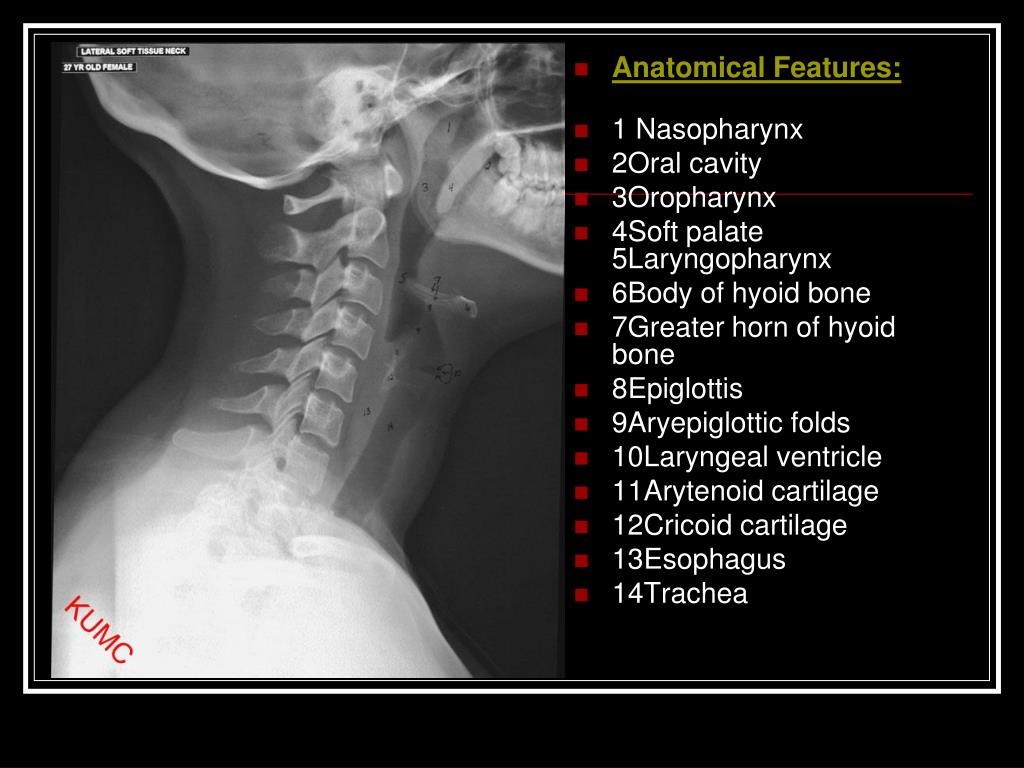
Labeled Soft Tissue Neck from KU Radiographic Anatomy Radiographic Anatomy Pinterest
Radiograph showing the soft tissues of the neck: lateral view. Name the areas labelled A-F that are important when looking at a radiograph in a patient with suspected ingestion of a foreign body ⇓. A: Epiglottis. Composed of fibrocartilage, it projects obliquely behind the base of the tongue, in front of the entrance to the larynx.
PPT Soft tissue neck PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6753069
Neck X-rays, also known as cervical spine X-rays, are a crucial diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to assess the condition of the neck and cervical spine. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of neck X-rays, including their uses, the procedure, and the valuable information they can provide.

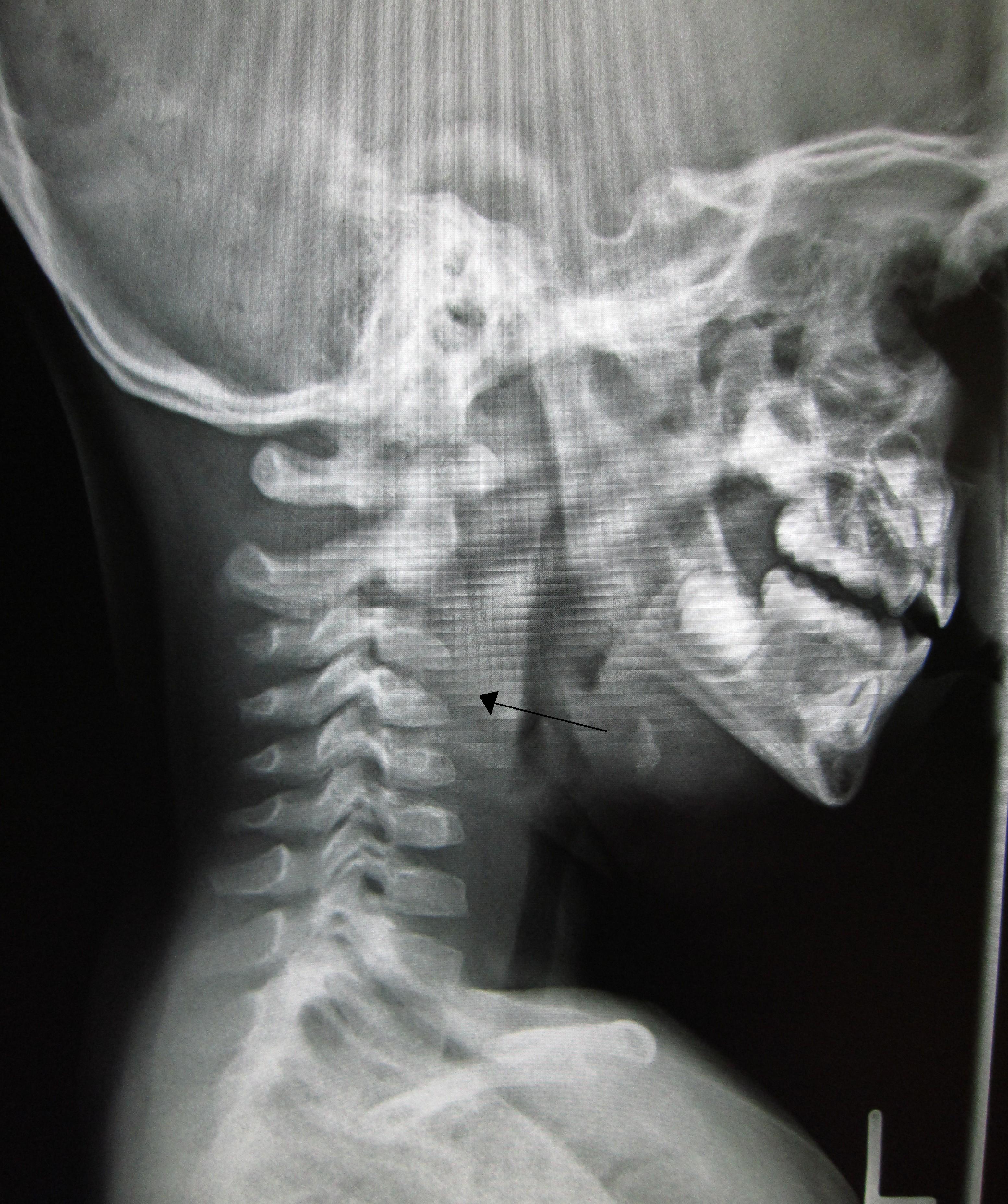
In a plain neck lateral film, an approximately 2cmsized radiopaque... Download Scientific
Soft tissue neck x-ray Normal delineation of the pharynx, larynx, and trachea. Paravertebral soft tissues demonstrate normal width, no evidence of foreign bodies or gas in the soft tissues. Cervical spine vertebral bodies have normal height and alignment. Case Discussion

Normal Neck, Xray Photograph by Du Cane Medical Imaging Ltd
Technique Radiograph of Neck obtained in anteroposterior and lateral projections. Findings No abnormal soft tissue noted in the nasopharynx and oropharynx. The prevertebral soft tissue appear normal. Visualised bones appears unremarkable. Impression No significant abnormality is seen. Go back Vision and Mission Investor Partnerships Sitemap

Imaging Soft Tissues of the Neck Radiology Key
X-ray Soft Tissue Neck Otorhinolaryngology Radiology Respiratory system Last modified: Jan 4, 2014 Anatomy: Plain X-ray Soft tissue lateral view neck. Normally, it shows: a. Outline of base of tongue. b. Vallecula. c. Hyoid bone. d. Epiglottis and aryepiglottic folds. e. Arytenoids. f. False and true cords with ventricle in between them. g.